Substituted amphetamines
Substituted amphetamines, also known as amphetamines, are a class of chemicals that include compounds with psychoactive effects.
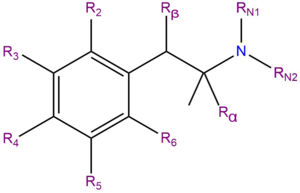
Chemistry
Substituted amphetamines are a chemical class based upon the molecule amphetamine. Amphetamine is made up of a phenethylamine molecule. The chemical structure of a substituted amphetamine is the same as the organic molecule amphetamine, except some substitutions are made at the phenyl and amine sites, typically of methyl and ethyl chains.
Pharmacology
The substituted amphetamine class of psychedelic, entactogenic and stimulant drugs works via their action upon numerous receptors. Psychedelic effects can be attributed to action on the 5-HT2A receptor. Entactogenic and stimulant effects are due to their action as releasing agents of serotonin, adrenaline and noradrenaline or as agonists on the receptors of the previous neurotransmitters. The agonism of this set of receptors leads to an increased rate firing of the post-synaptic neuron, triggering both cognitive and physical stimulation within the user.
List of substituted amphetamines
Note: This list does not include phenidates, cathinones, MDxxs, DOxs, Benzofurans or aminoindanes, nor does it contain any of the DMA or TMA isomers.
| Compound | R2 | R3 | R4 | R5 | R6 | Rα | Rβ | RN1 | RN2 | Structure |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Amphetamine | H | H | H | H | H | H | H | H | H | |
| Methamphetamine | H | H | H | H | H | H | H | H | CH3 | |
| Ethylamphetamine | H | H | H | H | H | H | H | H | CH3 | |
| Propylamphetamine | H | H | H | H | H | H | H | H | CH2CH2CH3 | |
| Isopropylamphetamine | H | H | H | H | H | H | H | H | CH2(CH3)2 | |
| Lisdexamfetamine | H | H | H | H | H | H | H | H | COCH(NH2)(CH2)4NH2 | |
| Clobenzorex | H | H | H | H | H | H | H | H | CH2C6H42Cl | |
| Dimethylamphetamine | H | H | H | H | H | H | H | CH3 | CH3 | |
| Selegiline | H | H | H | H | H | H | H | CH3 | CH2CCH | |
| Benzphetamine | H | H | H | H | H | H | H | CH3 | CH2C6H5 | |
| Ortetamine | CH3 | H | H | H | H | H | H | H | H | |
| 3-Methylamphetamine | H | CH3 | H | H | H | H | H | H | H | |
| 4-Methylamphetamine | H | H | CH3 | H | H | H | H | H | H | |
| 4-MMA | H | H | CH3 | H | H | H | H | H | CH3 | |
| Xylopropamine | H | CH3 | CH3 | H | H | H | H | H | H | |
| β-methylamphetamine | H | H | H | H | H | H | CH3 | H | H | |
| 2-FA | F | H | H | H | H | H | H | H | H | |
| 2-FMA | F | H | H | H | H | H | H | H | CH3 | |
| 3-FA | H | F | H | H | H | H | H | H | H | |
| 3-FMA | H | F | H | H | H | H | H | H | CH3 | |
| 3-FEA | H | F | H | H | H | H | H | H | CH2CH3 | |
| 4-FA | H | H | F | H | H | H | H | H | H | |
| 4-FMA | H | H | F | H | H | H | H | H | CH3 | |
| 4-CA | H | H | Cl | H | H | H | H | H | H | |
| 4-BA | H | H | Br | H | H | H | H | H | H | |
| 4-IA | H | H | I | H | H | H | H | H | H | |
| DCA | H | Cl | Cl | H | H | H | H | H | H | |
| 4-HA | H | H | OH | H | H | H | H | H | H | |
| 4-HMA | H | H | OH | H | H | H | H | H | CH3 | |
| 3,4-DHA | H | OH | OH | H | H | H | H | H | H | |
| OMA | OCH3 | H | H | H | H | H | H | H | H | |
| 3-MA | H | OCH3 | H | H | H | H | H | H | H | |
| MMMA | H | OCH3 | H | H | H | H | H | H | CH3 | |
| MMA | H | OCH3 | CH3 | H | H | H | H | H | H | |
| PMA | H | H | OCH3 | H | H | H | H | H | H | |
| PMMA | H | H | OCH3 | H | H | H | H | H | CH3 | |
| PMEA | H | H | OCH3 | H | H | H | H | H | CH2CH3 | |
| 4-ETA | H | H | OCH2CH3 | H | H | H | H | H | H | |
| 4-MTA | H | H | SCH3 | H | H | H | H | H | H | |
| Cathine | H | H | H | H | H | H | OH | H | H |
See also
References
This article does not cite enough references. You can help by adding some. |